The PE (worth to earnings ratio) of a inventory is eighteen. Is that low-cost or costly? Effectively, it relies upon. On what? Many issues! Welcome to the world of relative valuation.
The findings from analysis accomplished a decade earlier by Aswath Damodaran indicated that round 85 per cent of valuation accomplished by fairness analysis analysts and 50 per cent of company M&A transactions have been primarily based on relative valuation. So, what precisely is that this relative valuation?
It’s the artwork of making an attempt to find out the honest worth of a inventory primarily based on how it’s valued relative to many elements. So, whether or not the PE of a inventory is 15 or 18 or 30, the one means you can also make an evaluation of whether or not it’s low-cost or costly is by analysing this one quantity — towards its progress prospects, peer firm multiples, trade buying and selling vary, historic common PE, the prevailing rates of interest, and many others.

Portfolio podcast: The artwork of valuing shares
Portfolio podcast: The artwork of valuing shares
Let there be little doubt, valuation specialists like Aswath Damodaran and lots of profitable hedge fund managers imagine that absolute valuation (which we mentioned within the Massive Story in bl.portfolio version dated October 8) is the higher method to arrive on the worth of a inventory.
Nevertheless, as a consequence of a mixture of complexities concerned in constructing applicable fashions, inadequate info, time constraints and likewise the truth that there are lots of of shares you wish to think about, it’s simply not potential to do a DCF ( discounted money stream mannequin) for all of your inventory investments, and therefore relative valuation as an method to selecting shares too is properly accepted and broadly prevalent.
While you resolve to purchase or promote a inventory primarily based on its PE or P/B or EV/EBITDA or EV/Income and even EV/subscriber ratios, you’re partaking within the artwork of relative valuation. And it’s completely high quality to be an investor counting on relative valuation to make your financial savings give you the results you want, offered you method it the appropriate means and guarantee ample danger administration. In relative valuation, the broader you assess the valuation, ie assess valuation a number of towards extra parameters, the higher the attitude you get.
In easy phrases, one method to perceive the distinction between absolute valuation (defined in final week’s version) and relative valuation is that this – absolute valuation is made up of an attention-grabbing story that’s backed by credible and validated numbers, whereas relative valuation is made up of an attention-grabbing quantity backed by a reputable and validated story.
What are these numbers in relative valuation? Each quantity in relative valuation is the results of a quantity A divided by a quantity B. For instance, PE is worth of the inventory divided by its earnings. These are all numbers which can be used to match towards related metrics of different shares and assess the deserves of the inventory.
Earlier than we proceed on utilizing relative valuation to choose shares, you will need to perceive that you are able to do relative valuation utilizing fairness multiples or agency/enterprise multiples.
Fairness multiples
In case you examine the steadiness sheet of any firm, the liabilities aspect is primarily made up of two line objects — shareholder funds and borrowings. On the contrary, a Revenue and Loss assertion has many line objects — beginning with income, adopted by variable prices after which fastened prices and taxes. The one declare that fairness shareholders have for distribution or for appropriation amongst themselves is what’s left after paying the taxes — web revenue.
So, in case you are doing relative valuation primarily based on fairness multiples, you will need to make sure you divide the fairness – ie worth per share or market cap of the corporate by line objects that apply to fairness shareholders.
Primarily based on this, there are solely 3 objects that may be attributed to fairness shareholders — web revenue from P&L assertion, e-book worth or shareholder funds from the Steadiness Sheet, and the free money flows to fairness (FCFE) from the money stream assertion. Any relative valuation multiples will likely be linked to those three objects by some means. Another metric may very well be unsuitable and deceptive.
For instance, worth by income or worth by EBITDA is inaccurate. Why? How do you differentiate between two corporations A and B — each having identical market cap of ₹100 and related in all means aside from debt ranges — identical income (₹100) and identical gross margin and identical EBITDA margins of 20 per cent and thus identical EBITDA of ₹20. However A has zero debt, whereas B has debt of ₹10. Since income or gross sales and EBITDA are identical, when you do a market cap/income or Value /Gross sales, or marketcap/EBITDA, each corporations could have the identical valuation.
Nevertheless, let’s assume depreciation is ₹10, curiosity price is 10 per cent and taxes are zero. This implies the online revenue of A is ₹10, whereas that of B is ₹9. Thus though each corporations are related when it comes to Value/Income and Value/EBITDA, A is cheaper on the PE ratio – ie PE of A is 10 and PE of B is 11.1. On a relative valuation foundation, you have to select A as a substitute of B, however you wouldn’t have noticed it when you had used incorrect metrics.
Therefore it’s crucial to make use of the appropriate multiples. With regards to fairness metrics, it at all times must be worth or market cap (or variations of the identical) in numerator divided by line objects attributable to fairness holders (or variations of the identical)
The accompanying desk provides the generally used fairness multiples for relative valuation.
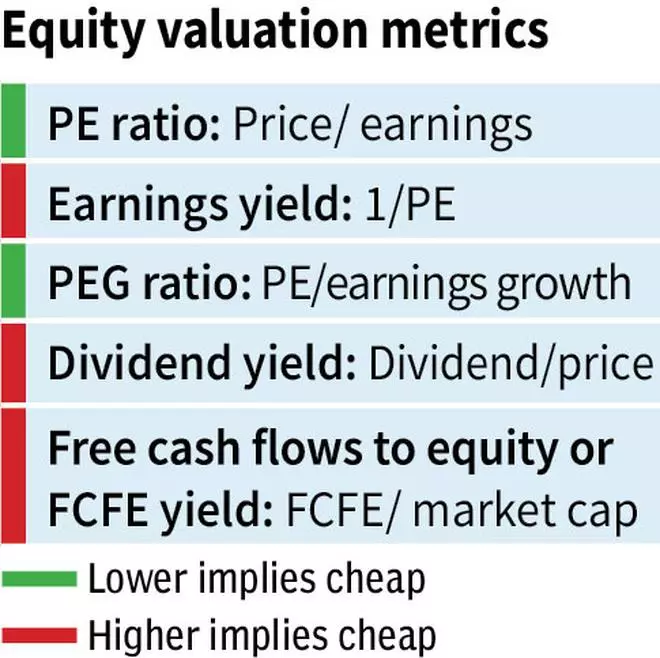
As soon as the metrics and significance are understood, there are, as such, no limits to how you should use them to choose shares. You should utilize one or two metrics or a mixture of many extra metrics to evaluate which shares are undervalued or overvalued.
Relying on particular instances, you should use additional variations to choose shares. For instance, in the course of the 2003-2007 bull market, many textile shares, as an example, Bombay Dyeing, turned out to be multibaggers. Was their textile enterprise booming? Not likely. However the shares have been zooming as a result of there was actual property growth and lots of textile mills had manufacturing services in prime actual property places. So the markets began to issue worth of the corporate primarily based on market worth of their land. In such a case you may deviate from Value/E book a number of to cost/market worth of web property (property – web debt).
Comparable is the case with holding corporations. In case you suppose there’s a affordable case for underlying worth of property to be unlocked and Holdco low cost to shrink, prefer it has occurred in financial institution holding corporations within the final 2-3 years, then there’s a case to maneuver past e-book worth to market worth.
Enterprise worth multiples
Enterprise worth refers to complete worth of an organization/enterprise. This complete worth as perceived by the market is represented by the sum of its market cap + web debt (contains minority curiosity). What works within the case of EV is that it helps in doing a capital-agnostic evaluation of an organization. Whether or not an organization is funded solely with fairness, or a mixture of fairness and debt, the whole worth of the enterprise is similar. Sources of funding don’t matter.
Utilizing EV, the worth of fairness (share worth) is derived from the worth of the enterprise. For the reason that capital construction of corporations varies considerably, an EV method allows valuing them on related phrases. One can arrive on the worth of the enterprise first after which subtract web debt, to reach on the fairness worth. The benefit with EV-based metrics is that you’ve extra choices to worth an organization.
Keep in mind, valuation accuracy is healthier the decrease down the P&L and money stream assertion one can get to. However there are a lot of occasions when firm earnings are low, however its operational efficiency ie EBITDA shouldn’t be dangerous. In such instances, as income and EBITDA proceed to develop, working leverage will end in PE rising a lot quicker than the above two line objects.
For instance, take the case of Bharti Airtel: firstly of FY22 (April ‘21) its trailing PE was unfavourable/invalid as a consequence of losses in FY21. The inventory would have been prevented if one glided by PE alone. Nevertheless, on trailing EV/EBITDA foundation, it was buying and selling at 10 occasions EV/EBITDA. When this was thought-about towards its estimated subsequent 2 years EBITDA CAGR of over 20 per cent, the valuation, mixed with qualitative elements, made it an attention-grabbing purchase. Since then, web earnings have improved considerably as working leverage performed out.
At bl.portfolio we had really useful a purchase on the inventory primarily based on this in April 2021 and the inventory has returned 80 per cent since. The inventory would have been simply missed if PE was the metric used to identify the performers.
Therefore EV-based metrics are choices to contemplate as properly when equity-based valuation multiples don’t give a transparent image. The place even EBITDA multiples usually are not clear, as was the case with many new-age firm IPOs that have been reporting losses even on the EBITDA degree, buyers haven’t any choice however to go additional up the P&L to metrics like EV/income, and even outdoors of P&L to make use of metrics like EV/subscriber.
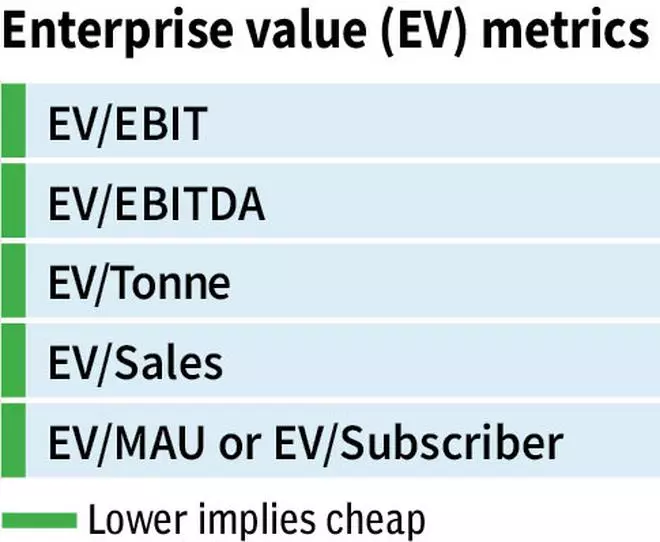
As we talked about earlier, relative valuation represents a quantity backed by a reputable and well-validated story. Therefore, you should use non-P&L multiples. So whenever you examine corporations and spend money on one primarily based on EV/Subscriber, there have to be a reputable story backing future monetisation of the subscriber in a worthwhile method. However do keep in mind, the dangers are larger and so often is the rewards or ache because the case could also be. When the dangers are larger, you have to apply the next margin of security earlier than selecting the inventory.
One other factor to keep in mind in relation to EV-based valuation — any change in EV will influence solely the fairness worth. For instance, if EV of an organization is ₹100 and it has ₹50 in debt, then the worth of its fairness is ₹50. On this case, when you suppose EV can enhance by 10 per cent, the worth of fairness will enhance by 20 per cent, and the reverse can be true. The upper the leverage, extra the influence of change in EV on the worth of the inventory (each methods).
Maintain a climate eye on Ketchup Economics
Given the truth that relative valuation relies on comparability with peer multiples, buyers should take measures to examine whether or not the peer multiples are affordable as properly. An overvalued peer can’t be used to justify costly valuation in a single inventory. That is what economist Larry Summers termed as Ketchup economists/economics. It was his sarcastic tackle among the extremely paid economists and finance professionals who’re involved solely with inter-relationships between costs of various monetary property. Primarily based on this method, they conclude whether or not the value of an asset independently is environment friendly or not. If two bottles of ketchup promote for twice as a lot as one bottle (aside from minor variations traceable to transaction prices), the market is environment friendly.
The chance on this – it ignores the facet of whether or not one bottle of ketchup is priced rationally. Nobel Laureate Paul Krugman as soon as defined how the US housing bubble that precipitated the worldwide monetary disaster reminded him of ketchup economists. Earlier than buying a home in the course of the bubble, patrons rigorously in contrast costs with ‘costs of different homes’, however ignored whether or not the general degree of a house worth made sense.
Learn how to keep away from pitfalls
So, what are you able to do to keep away from pitfalls whereas utilizing relative valuation? Listed here are just a few pointers.
One, after evaluating shares primarily based on relative valuation, you are able to do extra layers of comparability by assessing how their valuation fares relative to progress prospects. This aside, many different elements can justify totally different valuations. For instance, TCS has at all times commanded a valuation premium to see shares like Infosys, Wipro and HCLTech due to its superior margins and far more constant progress. So simply because the opposite shares are cheaper on PE foundation doesn’t imply they’re low-cost in comparison with TCS. So you too can do yet another layer of comparability by assessing every firm’s valuation towards its long-term (5-10 years) imply and median valuations and assess how they fare relative to their very own historical past.
Two, fairness valuations don’t operate in a silo. Buyers have many choices — fastened deposits, bonds, actual property, and many others. When different property get extra engaging one should assess scope for valuation change in equities as properly. For instance, rates of interest and bond yields in lots of developed markets, together with the US, are at their highest ranges since 2007. This implies buyers could must assess present valuations not simply towards final 10 years’ valuations, however of prior intervals as properly.
Why? Close to zero rates of interest and low bond yields made shares with earnings yield of mere 1-2 per cent engaging for an FPI — for instance shares reminiscent of Asian Paints, Nestle India and ABB India which at this time commerce at PE of 65, 83 and 85 occasions respectively. This means earnings yield of 1.5 per cent for Asian Paints and 1.2 per cent for Nestle and ABB. Such earnings yields of those shares have been high quality for FPIs to carry when in comparison with zero curiosity earnings of their home market. However now, with US bond yields providing 5 per cent, these will not be so engaging even when contemplating the expansion prospects. Whereas Indian rates of interest have been at all times larger, buyers in equities benefited from the worldwide buyers’ starvation for yields. That benefit is diminishing at this time. This isn’t a advice on the shares, however tips about elements to contemplate to make your relative valuation course of extra foolproof.
With self-discipline and expertise, the method will preserve getting higher.
#Basic #Investing #Artwork #Relative #Valuation
